Richard Feynman: "The result of the Michelson-Morley experiment was very puzzling and most disturbing. The first fruitful idea for finding a way out of the impasse came from Lorentz. He suggested that material bodies contract when they are moving, and that this foreshortening is only in the direction of the motion." https://www.feynmanlectures.caltech.edu/I_15.html
"Most disturbing" for etherists. For advocates of Newton's variable speed of light (e.g. Walther Ritz https://www.academia.edu/69646000/Ritz_Einstein_and_the_Emission_Hypothesis) the null result of the Michelson-Morley experiment meant victory of truth. Unfortunately, fraudsters are stronger than true scientists and the victory of truth often becomes humiliating defeat in the end.
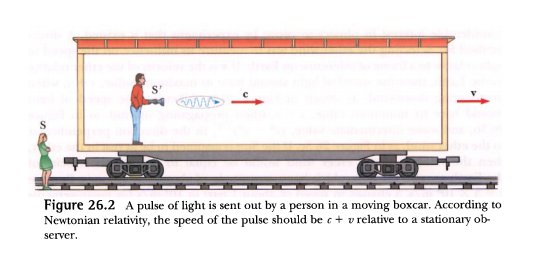
Originally, without Lorentz's "fruitful" fudge factor, the Michelson-Morley experiment was compatible with Newton's variable speed of light, c'=c±v, and incompatible with the constant speed of light, c'=c, posited by the ether theory and later adopted by Einstein as his 1905 second postulate:
"Emission theory, also called emitter theory or ballistic theory of light, was a competing theory for the special theory of relativity, explaining the results of the Michelson–Morley experiment of 1887...The name most often associated with emission theory is Isaac Newton. In his corpuscular theory Newton visualized light "corpuscles" being thrown off from hot bodies at a nominal speed of c with respect to the emitting object, and obeying the usual laws of Newtonian mechanics, and we then expect light to be moving towards us with a speed that is offset by the speed of the distant emitter (c ± v)." https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Emission_theory
"Moreover, if light consists of particles, as Einstein had suggested in his paper submitted just thirteen weeks before this one, the second principle seems absurd: A stone thrown from a speeding train can do far more damage than one thrown from a train at rest; the speed of the particle is not independent of the motion of the object emitting it. And if we take light to consist of particles and assume that these particles obey Newton's laws, they will conform to Newtonian relativity and thus automatically account for the null result of the Michelson-Morley experiment without recourse to contracting lengths, local time, or Lorentz transformations. Yet, as we have seen, Einstein resisted the temptation to account for the null result in terms of particles of light and simple, familiar Newtonian ideas, and introduced as his second postulate something that was more or less obvious when thought of in terms of waves in an ether." Banesh Hoffmann, Relativity and Its Roots, p.92 https://www.amazon.com/Relativity-Its-Roots-Banesh-Hoffmann/dp/0486406768
"Most disturbing" for etherists. For advocates of Newton's variable speed of light (e.g. Walther Ritz https://www.academia.edu/69646000/Ritz_Einstein_and_the_Emission_Hypothesis) the null result of the Michelson-Morley experiment meant victory of truth. Unfortunately, fraudsters are stronger than true scientists and the victory of truth often becomes humiliating defeat in the end.
Originally, without Lorentz's "fruitful" fudge factor, the Michelson-Morley experiment was compatible with Newton's variable speed of light, c'=c±v, and incompatible with the constant speed of light, c'=c, posited by the ether theory and later adopted by Einstein as his 1905 second postulate:
"Emission theory, also called emitter theory or ballistic theory of light, was a competing theory for the special theory of relativity, explaining the results of the Michelson–Morley experiment of 1887...The name most often associated with emission theory is Isaac Newton. In his corpuscular theory Newton visualized light "corpuscles" being thrown off from hot bodies at a nominal speed of c with respect to the emitting object, and obeying the usual laws of Newtonian mechanics, and we then expect light to be moving towards us with a speed that is offset by the speed of the distant emitter (c ± v)." https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Emission_theory
"Moreover, if light consists of particles, as Einstein had suggested in his paper submitted just thirteen weeks before this one, the second principle seems absurd: A stone thrown from a speeding train can do far more damage than one thrown from a train at rest; the speed of the particle is not independent of the motion of the object emitting it. And if we take light to consist of particles and assume that these particles obey Newton's laws, they will conform to Newtonian relativity and thus automatically account for the null result of the Michelson-Morley experiment without recourse to contracting lengths, local time, or Lorentz transformations. Yet, as we have seen, Einstein resisted the temptation to account for the null result in terms of particles of light and simple, familiar Newtonian ideas, and introduced as his second postulate something that was more or less obvious when thought of in terms of waves in an ether." Banesh Hoffmann, Relativity and Its Roots, p.92 https://www.amazon.com/Relativity-Its-Roots-Banesh-Hoffmann/dp/0486406768


