The speed of light VARIES with the speed of the emitter, as posited by Newton's theory
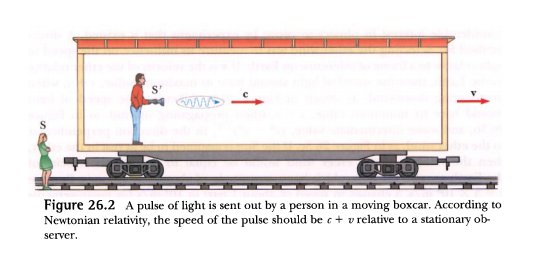
and unequivocally proved by the Michelson-Morley experiment:
"Emission theory, also called emitter theory or ballistic theory of light, was a competing theory for the special theory of relativity, explaining the results of the Michelson–Morley experiment of 1887...The name most often associated with emission theory is Isaac Newton. In his corpuscular theory Newton visualized light "corpuscles" being thrown off from hot bodies at a nominal speed of c with respect to the emitting object, and obeying the usual laws of Newtonian mechanics, and we then expect light to be moving towards us with a speed that is offset by the speed of the distant emitter (c ± v)." https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Emission_theory
Banesh Hoffmann, Einstein's co-author, admits that, originally ("without recourse to contracting lengths, local time, or Lorentz transformations"), the Michelson-Morley experiment was compatible with Newton's variable speed of light, c'=c±v, and incompatible with the constant speed of light, c'=c:
"Moreover, if light consists of particles, as Einstein had suggested in his paper submitted just thirteen weeks before this one, the second principle seems absurd: A stone thrown from a speeding train can do far more damage than one thrown from a train at rest; the speed of the particle is not independent of the motion of the object emitting it. And if we take light to consist of particles and assume that these particles obey Newton's laws, they will conform to Newtonian relativity and thus automatically account for the null result of the Michelson-Morley experiment without recourse to contracting lengths, local time, or Lorentz transformations. Yet, as we have seen, Einstein resisted the temptation to account for the null result in terms of particles of light and simple, familiar Newtonian ideas, and introduced as his second postulate something that was more or less obvious when thought of in terms of waves in an ether." Banesh Hoffmann, Relativity and Its Roots, p.92 https://www.amazon.com/Relativity-Its-Roots-Banesh-Hoffmann/dp/0486406768
It is easy to see that, given the formula
(speed of light) = (wavelength)(frequency)
variable speed of light as per Newton implies constant wavelength. If the death of physics is not irreversible, the fundamental axiom of future, Einstein-free physics will be
The wavelength of light is constant (depends only on the nature of the emitting substance and is constant otherwise).
Corollaries of "The wavelength of light is constant":
Corollary 1: Any frequency shift entails (is caused by) a proportional speed-of-light shift.
Corollary 2: If the emitter and the observer travel towards each other with relative speed v, the speed of light relative to the observer is c' = c+v, as posited by Newton's theory.
Corollary 3: Spacetime and gravitational waves (ripples in spacetime) don't exist. LIGO's "discoveries" are fakes.
Corollary 4: Light falls in a gravitational field with the same acceleration as ordinary falling bodies - near Earth's surface the accelerations of falling photons is g = 9.8 m/s^2. Accordingly, there is no gravitational time dilation.
Corollary 5: The so-called cosmological (Hubble) redshift is due to the speed of light gradually slowing down as light travels through vacuum, in a non-expanding universe.
Corollary 6: The dark sky in the Olbers' paradox can be explained by two facts. 1. Low-speed, high-redshifted light (known as CMB), coming from very distant sources, is invisible. 2. Beyond a certain distance, the star light does not reach us at all (its speed relative to us is reduced to zero).
and unequivocally proved by the Michelson-Morley experiment:
"Emission theory, also called emitter theory or ballistic theory of light, was a competing theory for the special theory of relativity, explaining the results of the Michelson–Morley experiment of 1887...The name most often associated with emission theory is Isaac Newton. In his corpuscular theory Newton visualized light "corpuscles" being thrown off from hot bodies at a nominal speed of c with respect to the emitting object, and obeying the usual laws of Newtonian mechanics, and we then expect light to be moving towards us with a speed that is offset by the speed of the distant emitter (c ± v)." https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Emission_theory
Banesh Hoffmann, Einstein's co-author, admits that, originally ("without recourse to contracting lengths, local time, or Lorentz transformations"), the Michelson-Morley experiment was compatible with Newton's variable speed of light, c'=c±v, and incompatible with the constant speed of light, c'=c:
"Moreover, if light consists of particles, as Einstein had suggested in his paper submitted just thirteen weeks before this one, the second principle seems absurd: A stone thrown from a speeding train can do far more damage than one thrown from a train at rest; the speed of the particle is not independent of the motion of the object emitting it. And if we take light to consist of particles and assume that these particles obey Newton's laws, they will conform to Newtonian relativity and thus automatically account for the null result of the Michelson-Morley experiment without recourse to contracting lengths, local time, or Lorentz transformations. Yet, as we have seen, Einstein resisted the temptation to account for the null result in terms of particles of light and simple, familiar Newtonian ideas, and introduced as his second postulate something that was more or less obvious when thought of in terms of waves in an ether." Banesh Hoffmann, Relativity and Its Roots, p.92 https://www.amazon.com/Relativity-Its-Roots-Banesh-Hoffmann/dp/0486406768
It is easy to see that, given the formula
(speed of light) = (wavelength)(frequency)
variable speed of light as per Newton implies constant wavelength. If the death of physics is not irreversible, the fundamental axiom of future, Einstein-free physics will be
The wavelength of light is constant (depends only on the nature of the emitting substance and is constant otherwise).
Corollaries of "The wavelength of light is constant":
Corollary 1: Any frequency shift entails (is caused by) a proportional speed-of-light shift.
Corollary 2: If the emitter and the observer travel towards each other with relative speed v, the speed of light relative to the observer is c' = c+v, as posited by Newton's theory.
Corollary 3: Spacetime and gravitational waves (ripples in spacetime) don't exist. LIGO's "discoveries" are fakes.
Corollary 4: Light falls in a gravitational field with the same acceleration as ordinary falling bodies - near Earth's surface the accelerations of falling photons is g = 9.8 m/s^2. Accordingly, there is no gravitational time dilation.
Corollary 5: The so-called cosmological (Hubble) redshift is due to the speed of light gradually slowing down as light travels through vacuum, in a non-expanding universe.
Corollary 6: The dark sky in the Olbers' paradox can be explained by two facts. 1. Low-speed, high-redshifted light (known as CMB), coming from very distant sources, is invisible. 2. Beyond a certain distance, the star light does not reach us at all (its speed relative to us is reduced to zero).


